Spatial audio specialists HOLOPHONIX have unveiled version 2.4.0, a major production release of its platform, alongside a suite of next-generation deep tech innovations currently in development that outline the future direction of spatial audio control, intelligence, and perception.
Together, these advancements mark a major step forward in precision, stability, interoperability, and intelligent spatial sound for live performance, immersive installations, and complex audio environments.
Version 2.4.0 is a production-ready update of the HOLOPHONIX platform, delivering substantial improvements across user experience, system reliability, interoperability, and architecture for live performance, installations, and permanent venues.
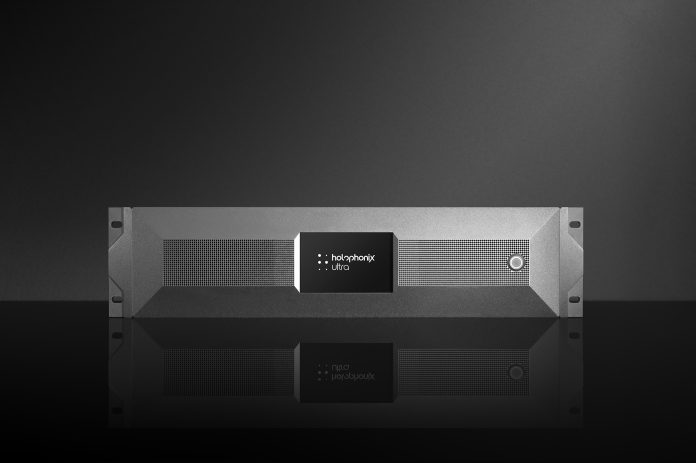
The release will be available for download shortly after ISE, at the end of February, and will be rolled out across all HOLOPHONIX platforms – from HOLOPHONIX Native to the full range of hardware processors, including the latest HOLOPHONIX Ultra.
“We have launched an ambitious R&D program with a clear objective: to keep HOLOPHONIX ahead of the curve and firmly establish it as one of the most advanced spatial audio platforms,” said Gaetan Byk, Owner, Founder and CEO at HOLOPHONIX.
“Version 2.4.0 already delivers substantial improvements and introduces key technologies such as the High-Order Ambisonics Convolution Engine and the Motion Engine for spatial composition and automation.
“But the most transformative innovations are still ahead. Upcoming developments include predictive electro-acoustic and immersive performance simulation, a camera-based headtracking application, the Speaker Locator hardware and software system, an AI Assistant natively integrated into HOLOPHONIX, and several other initiatives – many already being showcased in beta at ISE.”
Refined Interfaces for Professional Workflows
HOLOPHONIX 2.4.0 introduces a deeply refined user interface designed to improve clarity, responsiveness, and operational safety in real-world production environments.
New spatial reverb interfaces provide detailed control over Direct sound, Early reflections, and Late reverberation (cluster), enabling engineers to shape how sound propagates and is perceived within a space.
Mixer ergonomics have been significantly improved, with safety mechanisms that prevent accidental fader jumps, smoother parameter handling, and clearer feedback when editing multiple sound sources simultaneously.
Optimised interface virtualisation ensures smooth performance even in large-scale projects, while improved 3D navigation and standardized keyboard shortcuts accelerate everyday workflows.
High-Order Ambisonics Convolution Engine
Version 2.4.0 also introduces an advanced Convolution Reverb Engine capable of loading and processing Ambisonics-format impulse responses, enabling highly realistic and spatially coherent acoustic rendering.
The system is designed to preserve the true acoustic signature of real spaces. Users will be able to capture impulse responses in physical venues – such as churches, symphony halls or theatres – and process audio as if it were naturally occurring within those environments.
To support this, HOLOPHONIX is currently conducting dedicated measurement campaigns in prestigious venues, with the intention of integrating a curated library of real-world acoustic environments into the platform at a later stage.
Technically, this engine is designed to process High-Order Ambisonics impulse responses up to 64 channels (equivalent to 7th-order Ambisonics), offering an unprecedented level of spatial accuracy and creative flexibility.
Improved Stability and Audio Engine Reliability
At the core of version 2.4.0, the audio engine has been upgraded, resolving critical stability issues and improving long-term reliability for live shows and permanent installations.
Numerous fixes address routing inconsistencies, EQ artefacts, dynamics behaviour, and engine lifecycle management. The embedded platform has also been updated to reinforce system robustness and clarity during update and maintenance operations.
Open Standards and Interoperability
HOLOPHONIX 2.4.0 strengthens its commitment to open workflows through ADM-OSC v1 compliance, enabling improved interoperability with third-party immersive audio systems. ADM-OSC is now supported by a growing ecosystem of leading manufacturers and organizations, including d&b audiotechnik, L-Acoustics, Meyer Sound, Yamaha, Dolby, DiGiCo, Lawo, Merging Technologies, Steinberg, NEXO, Adamson, BBC, Radio France, and many others across the professional audio, broadcast and immersive technology sectors.
OSC routing, addressing, and data handling have been refined for greater consistency and predictability. Project and preset management have been redesigned with improved import/export workflows, duplication tools, CSV configuration exchange, and professional keyboard shortcuts.
“Interoperability is increasingly shaped by user expectations and by the evolution of professional workflows. Sound designers, engineers and operators need tools that integrate smoothly into heterogeneous environments rather than isolated ecosystems. Supporting ADM-OSC was therefore a natural step for us,” said Louis Genieys, Software Developer, HOLOPHONIX.
“With version 2.4.0, we focused on making our ADM-OSC implementation more robust and practical for real-world use: improved object and metadata handling, cleaner OSC addressing, more predictable routing behaviour, better project and preset exchange, and more reliable synchronization across external systems. The goal is not only to be compliant, but to also make interoperability actually usable on real productions,” continued Genieys.
“We validated this work through extensive real-world testing during the ADM-OSC PlugFest sessions hosted at Radio France, alongside manufacturers and organisations such as Yamaha, NEXO, Grapes 3D, TiMax, Naostage, d&b audiotechnik, L-Acoustics, Lawo, Adamson, Merging Technologies, Meyer Sound, BBC and Radio France.”
“These sessions are critical because they expose implementations to concrete use cases, edge cases and operational constraints. More broadly, this work also led us to rethink project management, data exchange and configuration tools inside HOLOPHONIX, so that the platform can integrate naturally into complex ecosystems spanning live production, broadcast and post-production workflows,” concluded Louis.
Motion Engine – Dynamic Sound Movement
The Motion Engine, currently under active development, introduces tools for creating generative and performance-driven movement of sound objects in space.
It allows artists and sound engineers to intuitively design paths and trajectories directly within the HOLOPHONIX interface, enabling efficient creation of movement within a scene.
From simple linear motions to advanced boids simulations, it supports a wide range of artistic intentions.
The engine opens new possibilities for live performance, installation art, and experimental spatial compositions, and is presented at ISE as an early-stage demonstration.
OEM Program
Alongside the 2.4.0 release, HOLOPHONIX is also expanding its presence through a dedicated OEM Program, designed for loudspeaker and electronics manufacturers seeking not only to integrate immersive and spatial audio into their product ecosystems, but also to explore new markets, create new vertical applications, and follow the growing momentum of immersive audio in live and experiential environments.
Partners gain access to the HOLOPHONIX technology stack while benefiting from extensive customisation possibilities, including branding options, custom GUI development, tailored I/O configurations, workflow adaptation, and optional bespoke feature development.
The OEM framework is designed to be highly flexible, allowing partners to define their own level of integration, from minor adaptations to fully customised solutions.
The core of the program is based on a dedicated hardware processor, the HOLOPHONIX Ultimate – a fully customized OEM platform developed for strategic manufacturing partners, built on the HOLOPHONIX Ultra technology stack and featuring a simplified, fully customisable hardware chassis designed to support deep product integration.
Educational Platform
HOLOPHONIX is developing an online educational platform offering e-learning content dedicated to its software, as well as broader resources on spatial audio and object-based mixing. Access to the platform will be free and available in both French and English.
A certification program is also in development, designed to further support users and recognise their expertise.
Next-Generation Spatial Audio Innovations Previewed at ISE 2026
Alongside the shipping release of version 2.4.0, HOLOPHONIX is showcasing a series of beta features and research developments at ISE 2026, reflecting its long-term work on intelligent and adaptive spatial audio systems.
These technologies are currently under development and are presented as previews of upcoming capabilities, including a camera-based headtracking plugin (beta), a predictive electro-acoustic simulation & immersive performance modelling software, motion engine (dynamic sound movement, in development), speaker locator, and AI assistant.
Camera-Based Headtracking
HOLOPHONIX is also presenting a beta version of a camera-based headtracking system, enabling listener-aware spatial audio rendering.
Using a standard webcam, the system tracks the orientation of the listener’s head and adapts binaural audio rendering accordingly.
This feature is intended for pre-production, demonstrations, and experimental workflows, particularly in binaural and headphone-based contexts.
“This feature originally came from a very concrete user demand. Many sound designers working in studio and pre-production want a more coherent and realistic binaural experience, where the rendering remains consistent when they move their head, rather than collapsing as soon as they turn slightly,” said Théo Ouchène, Research Engineer at HOLOPHONIX.
“With no headtracker needed, using a simple webcam, we can now continuously adapt the binaural rendering to the listener’s head orientation, which significantly improves localisation, stability, and externalisation compared to static binaural playback.
“This makes the tool particularly valuable for pre-production, remote listening, demonstrations, and creative exploration on headphones, where perceptual coherence is otherwise difficult to maintain.
“This first beta version is designed to be easily deployable in the HOLOPHONIX ecosystem. But this tool could evolve in many ways, depending on users. It might be used for systems beyond HOLOPHONIX or even integrate a complex binaural engine into it as a plugin (VST3, AU, etc.),” concluded Ouchène.
Predictive Electro-Acoustic Simulation & Immersive Performance Modelling
As part of its research-driven innovation, HOLOPHONIX is developing advanced predictive simulation tools designed not only to model electro-acoustic behaviour, but also to estimate perceptual listening quality and degree of immersion.
Based on precise loudspeaker measurements (Amadeus, and soon any CLF-compatible systems), spatial algorithms, and perceptual models, the system aims to predict key criteria such as localisation accuracy, timbral consistency, intelligibility, envelopment, and overall immersive performance across the audience area.
This approach enables engineers to evaluate and optimize system design before installation, moving beyond simple SPL mapping toward true experience-oriented system optimisation.
AI Assistant
HOLOPHONIX is introducing an AI Assistant embedded directly within the platform, designed to support users throughout both the creative and technical workflow.
The assistant allows users to interact with the system using natural language, helping accelerate complex tasks such as project setup, routing, parameter adjustments, scene organisation, and troubleshooting.
It is also designed to query the internal documentation and system knowledge (algorithms, signal flow, processing logic) to provide accurate technical guidance when needed.
Beyond assistance, the AI Assistant is being developed as an active design tool: it will be able to generate complex loudspeaker layouts in seconds, recommend appropriate spatialisation algorithms, and suggest optimized parameter settings based on the project context.
Connected via API to advanced large language models (LLMs), it provides contextual guidance, intelligent suggestions, and workflow assistance directly inside the HOLOPHONIX environment.
This feature is being developed as a practical productivity tool, aimed at reducing complexity while preserving full creative control for sound designers, engineers, and operators.
Speaker Locator
The Speaker Locator app uses advanced multi-channel signal processing to automatically detect, localise and validate loudspeaker positions, delivering accurate and repeatable 3D positioning across single or multiple measurement sessions.
It relies on Time of Arrival (TOA) and Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) analysis combined with Generalised Cross-Correlation with Phase Transform (GCC-PHAT) correlation and a constrained 3D triangulation engine, ensuring physically consistent localisation even in complex acoustic environments.
The system includes automatic outlier rejection and inter-session offset compensation, allowing reliable aggregation of measurements taken at different times or after microphone repositioning.
Final positions are consolidated and transmitted to HOLOPHONIX in real time via OSC, dramatically reducing manual positioning work while improving precision and repeatability.
“This tool allows us to reduce a task that used to take several hours to just a few minutes: accurately determining loudspeaker positions in a venue, whether during installation, calibration, touring setups or permanent installations,” said Adrien Zanni, CTO at HOLOPHONIX.
“Today, this process still relies heavily on manual workflows (SketchUp, AutoCAD layouts, laser measurements, etc.), with a complexity that becomes exponential as system density increases, and quickly becomes unmanageable when dealing with hundreds of loudspeakers.
“With our new algorithms, combined with a simple setup using four omnidirectional microphones, a 3D-printed mounting rig ensuring precise capsule geometry, and standard MLS or sweep measurement signals, we are now able to automatically and accurately detect loudspeaker positions within minutes, using lightweight and affordable hardware,” concluded Zanni.
Research & Development: Exploring the Future of Spatial Audio
“At HOLOPHONIX, we are deeply invested in long-term research around some of the most complex challenges in spatial audio today: active acoustics and regenerative systems, advanced beamforming and sound zone control, and low-frequency active acoustic absorption. These are not theoretical topics for us, but concrete technologies we are actively developing to reshape how sound behaves in real spaces,” added Zanni.
These R&D initiatives place HOLOPHONIX at the intersection of applied research, artistic experimentation, and professional audio engineering.
At ISE 2026, HOLOPHONIX demonstrates not only what spatial audio can deliver today, but where it is headed next.